SSL and HTTP
SSL and HHTP is an open, non-proprietary protocol that perhaps constitutes the most common way of providing encrypted transmission of data between web browsers and web servers (HTTP-S). Built upon private key encryption technology, SSL provides data encryption, server authentication, message integrity, and client authentication for any TCP/IP connection.
For our purposes, SSL provides these services between SSL-enabled browsers and SSL-enabled servers. Most of commercial web browsers provide native built-in support to SSL.
From the developer's stand-point there no difference between developing a web site for https or http. The implementation of the SSL on a server is an administrative task and corresponds to the company's security policy.
How can a user find out if a web site security is enabled?
Any end user is able to find out if the web site contacted is encrypting the information exchange or ensuring that the web site actually corresponds to the company it wants to connect to. In order to find out, look for the right bottom padlock icon on the right of your browser window.
![]()
How can I find out the authenticity of the certificate?
Double-click on the padlock icon. An information certificate window will pop up.
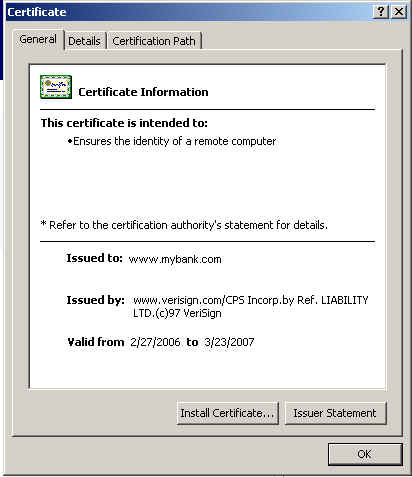
This certificate not only ensures that the information you exchange is sent securely encrypted but also that web site belongs to a legitimate source. Legitimate certificate bearer is a company that has gone through an exhaustive screening process .
Is it possible that a certificate bearer publish a non-valid certificate?.
Yes, it's possible that a company has it's own Certification Authority software that makes the able to create their own certificates with no previous third-party screening process. If this is the case, when you connect to such web site, the browser will warn you about the possible illegitimate source of the certificate bearer.
Security checklist.
1. Always check if the padlock is present.
2. If so, take your time to review the certificate.
3. A secure web site should not give you any warning or error message.
4. Check the source of the certificate at the "Issued to" item. It must be web site's url of the site you are visiting.
5. The "Issued by" item shows the certification authority. Any warning or error message at this item, means that the certification authority that issued this certificate is not secure and you might be a victim of a session jacking.
6. The "Valid from" item must be always valid at the present time.